Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) affects millions of people worldwide, often progressing silently until it reaches a critical stage. Understanding the 5 stages of Chronic Kidney Disease is crucial for early detection, effective management, and improved patient outcomes. At SHINING LIGHT HOSPICE, we are committed to providing comprehensive care and support for individuals at every stage of CKD. This article delves into the intricacies of CKD, outlining each stage and offering practical advice for patients and caregivers.
What is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
Definition of CKD: Chronic Kidney Disease is a long-term condition characterized by a gradual loss of kidney function over time. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, and when their function is compromised, it can lead to severe health issues.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can strain the kidneys, leading to damage.
- Genetic Factors: Family history can increase the risk of CKD.
- Other Medical Conditions: Conditions like glomerulonephritis and polycystic kidney disease can also cause CKD.
Prevalence and Statistics: CKD affects approximately 10% of the global population. In the United States alone, nearly 37 million people are estimated to have CKD. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital in managing the disease and preventing its progression.
The Role of the Kidneys in the Body
Functions of the Kidneys:
- Filtration of Blood: Removing waste and excess fluids.
- Regulation of Electrolytes: Balancing sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes.
- Blood Pressure Control: Regulating blood pressure through fluid balance.
- Hormone Production: Producing hormones like erythropoietin, which stimulates red blood cell production.
Impact of Impaired Kidney Function: When kidney function is impaired, waste products and excess fluids can build up in the body, leading to complications such as high blood pressure, anemia, and cardiovascular diseases.
Detailed Breakdown of the 5 Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
Stage 1: Kidney Damage with Normal or High GFR (90 or Above)
Description and Symptoms:
- Normal kidney function with signs of damage.
- Often asymptomatic, but proteinuria or physical abnormalities may be present.
Diagnostic Criteria:
- GFR: ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m²
Management and Lifestyle Recommendations:
- Regular monitoring of kidney function.
- Controlling blood pressure and blood sugar levels.
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Case Study: Meet M Sumon, a 40-year-old diagnosed with Stage 1 CKD during a routine check-up. Through lifestyle changes and regular monitoring, John has maintained his kidney function and avoided progression to later stages.
Stage 2: Mild Decrease in GFR (60-89)
Description and Symptoms:
- Slight reduction in kidney function.
- Mild kidney damage with minimal or no symptoms.
Diagnostic Criteria:
- GFR: 60-89 mL/min/1.73 m²
Management and Lifestyle Recommendations:
- Regular check-ups to monitor kidney function.
- Addressing underlying conditions like hypertension and diabetes.
- Dietary adjustments to reduce kidney workload.
Case Study: Sarah, a 48-year-old with Stage 2 CKD, manages her condition through a kidney-friendly diet and medication, preventing further decline in kidney function.
Stage 3: Moderate Decrease in GFR (30-59)
Description and Symptoms:
- Moderate reduction in kidney function.
- Symptoms such as swelling, fatigue, and changes in urination may appear.
Diagnostic Criteria:
- GFR: 30-59 mL/min/1.73 m²
Management and Lifestyle Recommendations:
- Detailed evaluation by a nephrologist.
- Strict blood pressure and glucose control.
- Medications to manage symptoms and slow progression.
- Dietary changes to manage phosphorus, potassium, and protein intake.
Differences between Stage 3a and 3b:
- Stage 3a: GFR 45-59 mL/min/1.73 m²
- Stage 3b: GFR 30-44 mL/min/1.73 m²
Case Study: Mike, at Stage 3b, experiences fatigue and swelling. Through medication and a specialized diet, he manages his symptoms and maintains his quality of life.
Stage 4: Severe Decrease in GFR (15-29)
Description and Symptoms:
- Severe reduction in kidney function.
- More pronounced symptoms, including anemia, bone disease, and cardiovascular complications.
Diagnostic Criteria:
- GFR: 15-29 mL/min/1.73 m²
Management and Lifestyle Recommendations:
- Preparing for potential dialysis or kidney transplant.
- Aggressive management of blood pressure and diabetes.
- Nutritional counseling to address specific needs.
- Close monitoring and treatment of complications.
Case Study: Linda, at Stage 4, prepares for a kidney transplant. With the support of her healthcare team, she manages her symptoms and remains hopeful for a successful transplant.
Stage 5: Kidney Failure (GFR <15 or on Dialysis)
Description and Symptoms:
- End stage of CKD, where the kidneys have lost nearly all their ability to function.
- Symptoms include severe fatigue, nausea, and swelling.
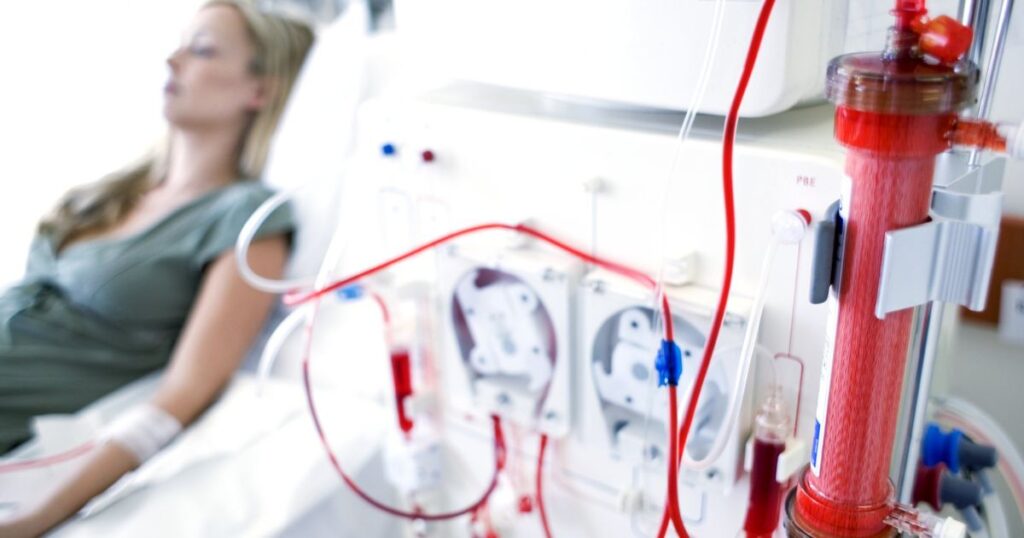
Diagnostic Criteria:
- GFR: <15 mL/min/1.73 m² or on dialysis
Management and Lifestyle Recommendations:
- Dialysis or kidney transplant to replace lost kidney function.
- Comprehensive management of complications.
- Supportive care to improve quality of life.
Case Study: Tom, in Stage 5, receives dialysis three times a week. Despite the challenges, he maintains a positive outlook with the help of his healthcare team and supportive family.
Diagnosing CKD (Chronic Kidney Disease)
Common Tests and Procedures:
- Blood Tests: Measure creatinine and estimate GFR.
- Urine Tests: Detect proteinuria.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound and CT scans to assess kidney structure.
- Kidney Biopsy: Determine the type and extent of kidney damage.
Importance of Regular Screening for High-Risk Individuals: Regular screening for those with risk factors like diabetes, hypertension, and family history of CKD is essential for early detection and intervention.
Managing CKD at Different Stages
Medical Management:
- Medications: To control blood pressure, blood sugar, and manage symptoms.
- Treatment of Complications: Address anemia, bone disease, and cardiovascular issues.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Diet and Nutrition: Low-sodium, low-protein diet to reduce kidney workload.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Regular physical activity to maintain overall health.
- Avoiding Nephrotoxic Substances: Limiting use of NSAIDs and other nephrotoxic drugs.
Patient Education and Support:
- Providing comprehensive information about CKD and its management.
- Support groups and counseling for emotional and mental health.
Living with CKD
Psychosocial Aspects:
- Coping with a CKD diagnosis and its impact on daily life.
- Mental health support through counseling and support groups.
Quality of Life Improvements:
- Importance of adherence to treatment plans.
- Engaging in healthy activities and hobbies.
- Building a support system with family, friends, and healthcare providers.
The Role of Hospice Care in CKD
Introduction to Hospice Care: Hospice care provides compassionate support for individuals with advanced CKD, focusing on quality of life and comfort.
Services Provided by SHINING LIGHT HOSPICE:
- Pain and Symptom Management: Alleviating discomfort and managing symptoms.
- Emotional and Spiritual Support: Offering counseling and spiritual care.
- Caregiver Support: Assisting caregivers with resources and respite care.
- End-of-Life Care Planning: Helping families navigate end-of-life decisions.
Understanding the 5 stages of Chronic Kidney Disease is crucial for early detection and effective management. At SHINING LIGHT HOSPICE, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive care and support to help patients navigate their CKD journey. For more information or to schedule an appointment, visit our website at www.shininglighthospice.com or contact us at:
SHINING LIGHT HOSPICE
3265 N. Fort Apache Rd, Suite 150, Las Vegas, NV 89129
Email: [email protected]
Phone: 702-906-0044
Together, we can shine a light on better kidney health.
References and Resources
Links to Further Reading:
- National Kidney Foundation – About Chronic Kidney Disease
- Mayo Clinic – Chronic Kidney Disease
- American Kidney Fund – Kidney Disease Stages
- WebMD – Chronic Kidney Disease
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Chronic Kidney Disease Initiative
Acknowledgments:
- We would like to thank the medical professionals at SHINING LIGHT HOSPICE for their invaluable insights and contributions to this article.
- Special thanks to Dr. Zeeshan F. Syed, Nephrologist, for her expert review and guidance.
- Appreciation to the National Kidney Foundation for their comprehensive resources on CKD.






